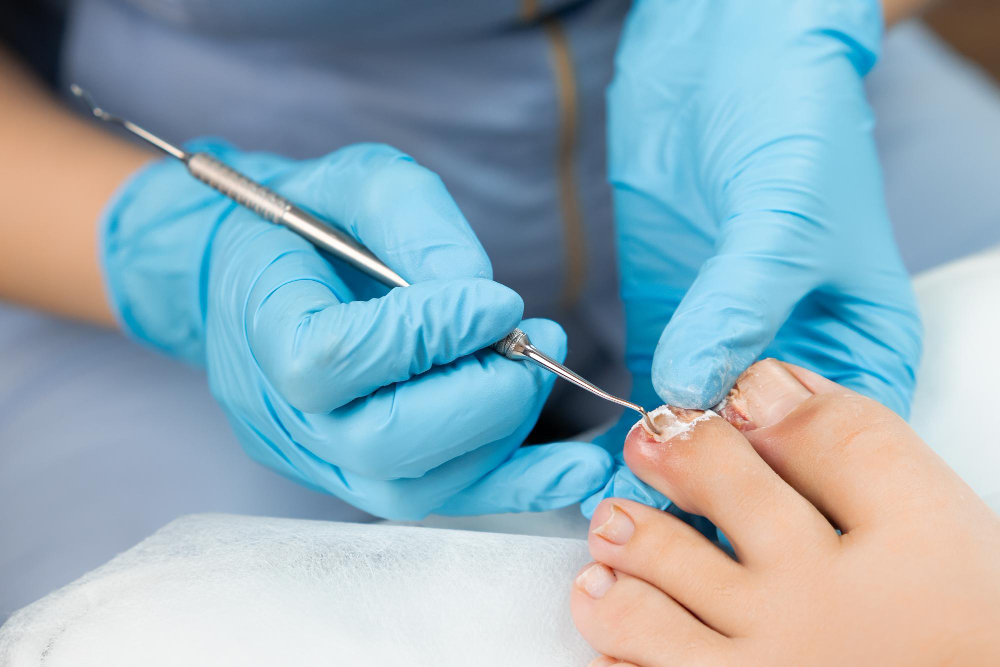
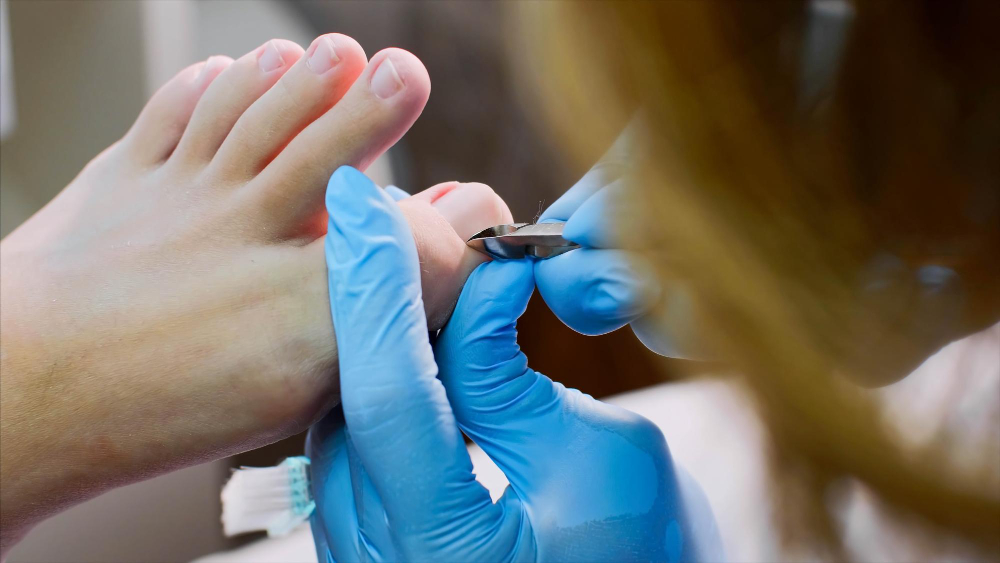
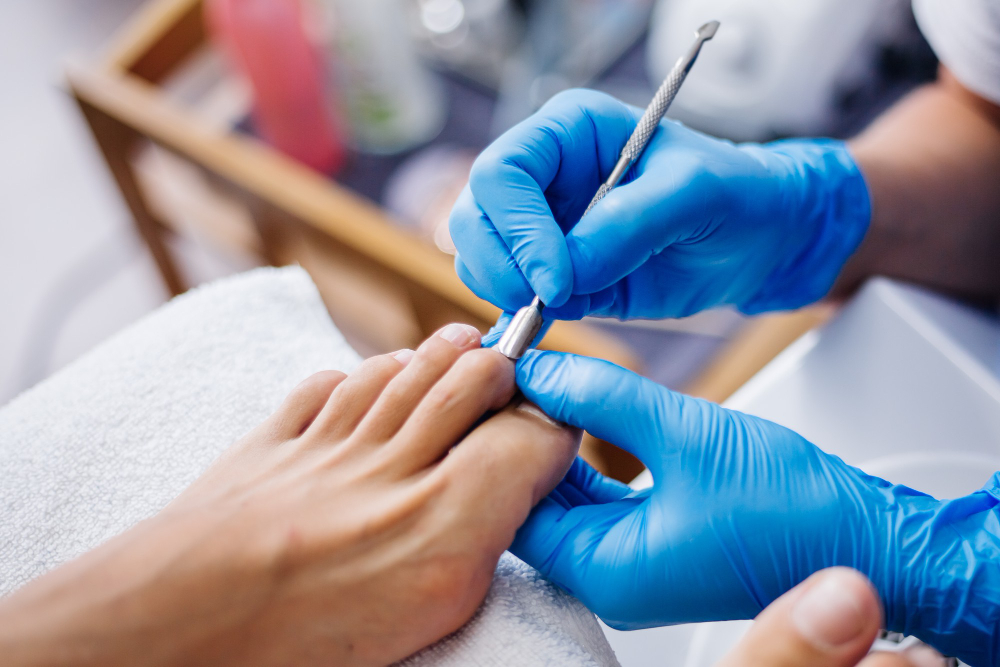
What Causes Ingrown Toenails :
Ingrown toenails, a common and often painful condition, occur when the edge of a toenail grows into the surrounding skin instead of over it. This condition can lead to redness, swelling, and discomfort. Understanding the causes and recognizing the signs of ingrown toenails is essential to prevent their occurrence and seek timely treatment. In this blog post, we will explore the primary causes of ingrown toenails and the signs to be aware of.
- Improper Nail Trimming: One of the primary causes of ingrown toenails is improper nail trimming. Cutting your toenails too short or rounding the edges can encourage the surrounding skin to fold over the nail, leading to ingrowth. It’s important to trim your toenails straight across to prevent this problem. Avoid curving the edges and keep them at a length that doesn’t dig into the skin.
- Tight-Fitting Shoes:Wearing tight shoes, especially those that compress the toes and put pressure on the nails, is a significant contributor to ingrown toenails. Tight shoes can force the nail to grow into the skin instead of outward, causing pain and irritation. Choosing shoes that provide adequate room for your toes and proper support can reduce the risk of ingrown toenails.
- Injury or Trauma:Injuries to the toenail or the surrounding area can cause ingrown toenails. Stubbing your toe, dropping heavy objects on your foot, or any other form of trauma can lead to changes in the nail’s growth pattern. The nail may start growing abnormally, causing it to penetrate the adjacent skin. Be cautious and seek medical attention if you experience any trauma to your toenails.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to developing ingrown toenails. If ingrown toenails are common in your family, you may have inherited the tendency. Genetics can influence the shape and structure of your toenails, making you more susceptible to this condition. Regular foot care and proper nail trimming become crucial preventive measures for those with a family history of ingrown toenails.
- Fungal or Bacterial Infections: Fungal or bacterial infections of the toenail or the surrounding skin can also contribute to the development of ingrown toenails. Infections can distort the natural growth of the nail and cause it to grow inappropriately, leading to ingrowth. Maintaining good foot hygiene and promptly treating any signs of infection can help prevent this cause of ingrown toenails.
Signs to Watch Out For:
- Pain and Tenderness: If you experience persistent pain and tenderness around the edge of your toenail, it could be a sign of an ingrown toenail. The discomfort may increase when pressure is applied to the area, such as when wearing tight shoes.
- Redness and Swelling: Ingrown toenails often cause redness and swelling around the affected area. The skin may become inflamed as it reacts to the nail piercing through or growing into it.
- Pus or Drainage: An ingrown toenail can lead to infection, resulting in the formation of pus or drainage around the affected nail. If you notice any discharge or a foul odor, it’s important to seek medical attention.
- Difficulty Walking or Wearing Shoes: As the ingrown toenail worsens, it may become increasingly difficult to walk or wear shoes comfortably due to the pain and pressure on the affected toe.
- Visible Nail Overgrowth: Sometimes, ingrown toenails may be accompanied by visible nail overgrowth. The nail may appear to have grown into the skin or have sharp edges.
Understanding the causes and recognizing the signs of ingrown toenails is crucial for early intervention and prevention. If you suspect you have an ingrown toenail or are experiencing persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment to alleviate pain and prevent complications.
.
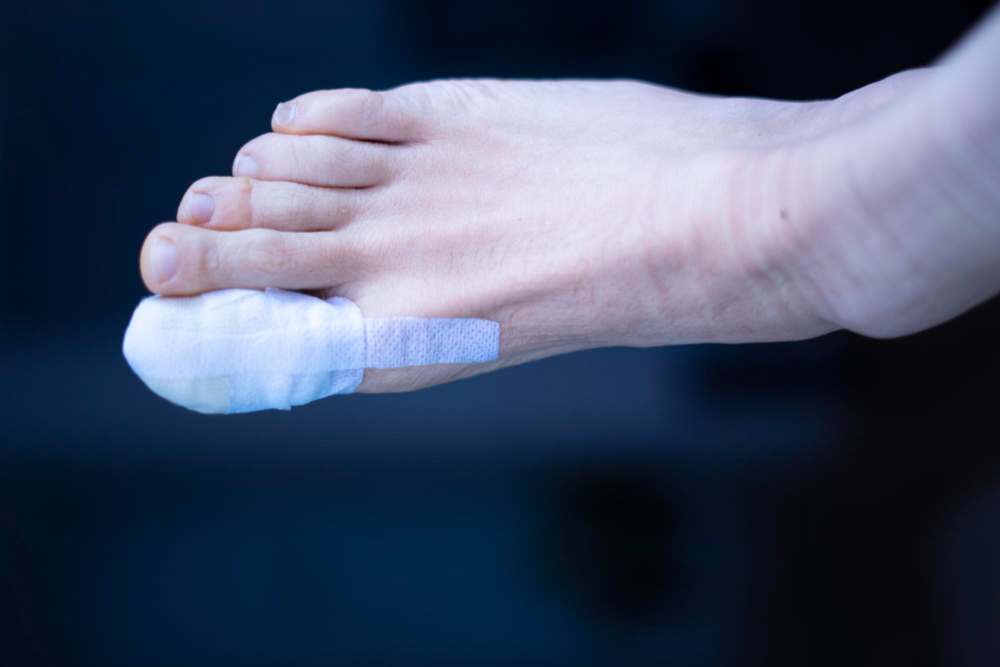
Aftercare Tips and Recovery:
Effective postoperative care is crucial for speedy recovery and preventing complications following toenail surgery. This section outlines important aftercare tips, such as keeping the foot clean and dry, applying topical medications or dressings as directed, managing pain and swelling, and monitoring for signs of infection. Additionally, individuals will find guidance on when to seek medical attention during the recovery period.
Preventing Ingrown Toenails in the Future:
While toenail surgery effectively treats ingrown nails, it is ideal to prevent their occurrence altogether. Recommendations include proper nail trimming techniques, wearing appropriate footwear, maintaining good foot hygiene, and seeking professional help for any foot abnormalities or recurring issues.
By following these guidelines and understanding the surgical procedure and aftercare tips, individuals can find relief from ingrown toenails and reduce the likelihood of future occurrences. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options based on individual needs